改這個檔 /etc/squid/squid.conf
allow 內網可以透過 proxy
就放在那個 INSERT YOUR ….
acl officenet src 172.30.0.0/24 http_access allow officenet
改這個檔 /etc/squid/squid.conf
allow 內網可以透過 proxy
就放在那個 INSERT YOUR ….
acl officenet src 172.30.0.0/24 http_access allow officenet
A database administrator (DBA) is a person who is responsible for the environmental aspects of a database. The role of a database administrator has changed according to the technology of database management systems (DBMSs) as well as the needs of the owners of the databases. For example, although logical and physical database design are traditionally the duties of a database analyst or database designer, a DBA may be tasked to perform those duties.
Duties
The duties of a database administrator vary and depend on the job description, corporate and Information Technology (IT) policies and the technical features and capabilities of the DBMS being administered. They nearly always include disaster recovery (backups and testing of backups), performance analysis and tuning, data dictionary maintenance, and some database design.
Some of the roles of the DBA may include
- Installation of new software — It is primarily the job of the DBA to install new versions of DBMS software, application software, and other software related to DBMS administration. It is important that the DBA or other IS staff members test this new software before it is moved into a production environment.
- Configuration of hardware and software with the system administrator — In many cases the system software can only be accessed by the system administrator. In this case, the DBA must work closely with the system administrator to perform software installations, and to configure hardware and software so that it functions optimally with the DBMS.
- Security administration — One of the main duties of the DBA is to monitor and administer DBMS security. This involves adding and removing users, administering quotas, auditing, and checking for security problems.
- Data analysis — The DBA will frequently be called on to analyze the data stored in the database and to make recommendations relating to performance and efficiency of that data storage. This might relate to the more effective use of indexes, enabling "Parallel Query" execution, or other DBMS specific features.
- Database design (preliminary) — The DBA is often involved at the preliminary database-design stages. Through the involvement of the DBA, many problems that might occur can be eliminated. The DBA knows the DBMS and system, can point out potential problems, and can help the development team with special performance considerations.
- Data modeling and optimization — By modeling the data, it is possible to optimize the system layouts to take the most advantage of the I/O subsystem.
- Responsible for the administration of existing enterprise databases and the analysis, design, and creation of new databases.
- Data modeling, database optimization, understanding and implementation of schemas, and the ability to interpret and write complex Structured Query Language (SQL) queries
- Proactively monitor systems for optimum performance and capacity constraints
- Establish standards and best practices for SQL
- Interact with and coach developers in SQL scripting
URL : http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.html#formats
我的 sample code :
ServerName test.monster.tw
DocumentRoot "/m2/test"
LogFormat "%{%Y-%m-%d}t , %{%H:%M:%S}t , %D , %a , \"%q\" , \"%{Referer}i\" , \"%{User-agent}i\"" MONSTER_format
CustomLog "/m2/log/test.monster.tw/access.log" MONSTER_format
MTS 的 http config
SetEnvIf Request_URI /dot.gif MTS_icon
LogFormat "%{%Y-%m-%d}t , %{%H:%M:%S}t , %a , \"%q\" , \"%{Referer}i\" , \"%{User-agent}i\"" MTS_format
CustomLog "| /usr/sbin/cronolog /var/www/ts.monster.com.tw/log/access-%Y%m%d%H.log" MTS_format env=MTS_icon
apache default 的 combined format
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-agent}i\"" combined
CustomLog log/acces_log combined
以下是 apache 的資料
| Format String | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
%% |
The percent sign | ||||||
%a |
Remote IP-address | ||||||
%A |
Local IP-address | ||||||
%B |
Size of response in bytes, excluding HTTP headers. | ||||||
%b |
Size of response in bytes, excluding HTTP headers. In CLF format, i.e. a ‘-‘ rather than a 0 when no bytes are sent. |
||||||
%{Foobar}C |
The contents of cookie Foobar in the request sent to the server. | ||||||
%D |
The time taken to serve the request, in microseconds. | ||||||
%{FOOBAR}e |
The contents of the environment variable FOOBAR | ||||||
%f |
Filename | ||||||
%h |
Remote host | ||||||
%H |
The request protocol | ||||||
%{Foobar}i |
The contents of Foobar: header line(s) in the request sent to the server. Changes made by other modules (e.g. mod_headers) affect this. |
||||||
%k |
Number of keepalive requests handled on this connection. Interesting if KeepAlive is being used, so that, for example, a ‘1’ means the first keepalive request after the initial one, ‘2’ the second, etc…; otherwise this is always 0 (indicating the initial request). |
||||||
%l |
Remote logname (from identd, if supplied). This will return a dash unless mod_ident is present and IdentityCheck is set On. |
||||||
%m |
The request method | ||||||
%{Foobar}n |
The contents of note Foobar from another module. | ||||||
%{Foobar}o |
The contents of Foobar: header line(s) in the reply. |
||||||
%p |
The canonical port of the server serving the request | ||||||
%{format}p |
The canonical port of the server serving the request or the server’s actual port or the client’s actual port. Valid formats are canonical, local, or remote. |
||||||
%P |
The process ID of the child that serviced the request. | ||||||
%{format}P |
The process ID or thread id of the child that serviced the request. Valid formats are pid, tid, and hextid. hextid requires APR 1.2.0 or higher. |
||||||
%q |
The query string (prepended with a ? if a query string exists, otherwise an empty string) |
||||||
%r |
First line of request | ||||||
%s |
Status. For requests that got internally redirected, this is the status of the *original* request — %>s for the last. |
||||||
%t |
Time the request was received (standard english format) | ||||||
%{format}t |
The time, in the form given by format, which should be in strftime(3) format. (potentially localized) |
||||||
%T |
The time taken to serve the request, in seconds. | ||||||
%u |
Remote user (from auth; may be bogus if return status (%s) is 401) |
||||||
%U |
The URL path requested, not including any query string. | ||||||
%v |
The canonical ServerName of the server serving the request. |
||||||
%V |
The server name according to the UseCanonicalName setting. |
||||||
%X |
Connection status when response is completed:
(This directive was |
||||||
%I |
Bytes received, including request and headers, cannot be zero. You need to enable mod_logio to use this. |
||||||
%O |
Bytes sent, including headers, cannot be zero. You need to enable mod_logio to use this. |
防止盜圖的 code
SetEnvIf Referer "^http://www.example.com/" local_referal # Allow browsers that do not send Referer info SetEnvIf Referer "^$" local_referal [directory images web] Order Deny,Allow Deny from all Allow from env=local_referal [/directory]
這個更讚! 排除掉 gif / jpg / png / css / swf … 等等不要log的檔案
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.gif misc-request SetEnvIf Request_URI \.jpg misc-request SetEnvIf Request_URI \.png misc-request SetEnvIf Request_URI \.css misc-request SetEnvIf Request_URI \.swf misc-request CustomLog logs/access_log env=!misc-request
整合一下, 這是 lazy 的 config
ServerName lazy.monster.tw
DocumentRoot "/home/webuser/lazy.monster.tw"
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.gif misc-request
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.jpg misc-request
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.png misc-request
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.css misc-request
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.swf misc-request
LogFormat "%{%Y-%m-%d}t , %{%H:%M:%S}t , %a , %u , %D , \"%r\" , \"%{Referer}i\" , \"%{User-agent}i\"" MONSTER_format
CustomLog /m2/log/lazy.monster.tw/access.log MONSTER_format env=!misc-request
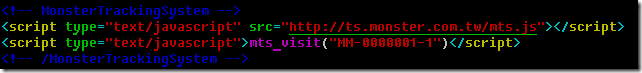
mts.js , 網上範例很多 , 這個是基本型: ![]()
這段 code 前面就是一連串的組出 z 變數(包括 OS , BROWSER , SCREEN WIDTH/HEIGHT …) , 然後用一個小點透過 apache 的 log 記錄下來.
這個 apache 要裝 mod_setenvif 或 mod_rewrite modules , 在 apache config 中設定 只 log 特定的 tracking data.
SetEnvIf Request_URI /dot.gif MTS_icon
LogFormat "%{%Y-%m-%d}t , %{%H:%M:%S}t , %a , \"%q\" , \"%{Referer}i\" , \"%{User-agent}i\"" MTS_format
CustomLog "| /usr/sbin/cronolog /var/www/ts.monster.com.tw/log/access-%Y%m%d%H.log" MTS_format env=MTS_icon
引用例:
然後 apache log 會長這個樣子:

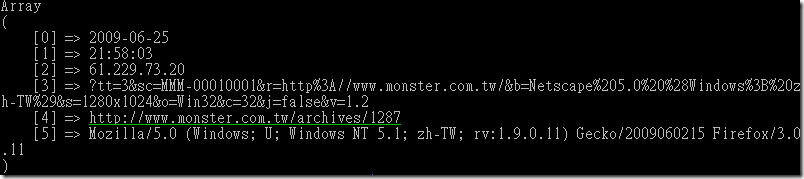
寫一段 PHP code:
$fp = fopen($mts_logfile,"r");
while ( $temp = fgetcsv($fp,$max_size) ) {
if ( count($temp)<1 ) continue;
print_r($temp);
}
fclose($fp);
結果就類似這樣:
再來就是處理 [3] 那邊的各種 data …
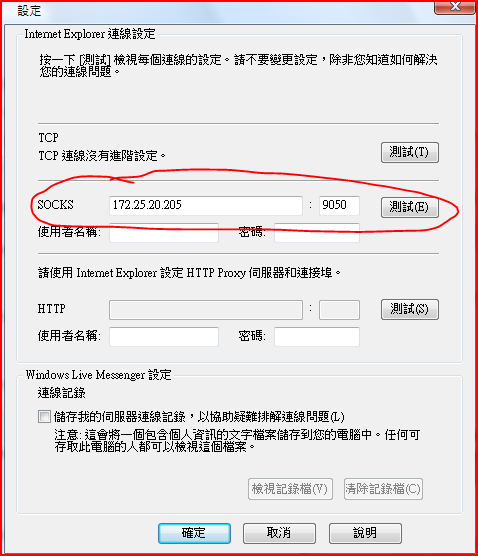
要先裝好 tor , 啟動 tor 後 , 用 putty 照下面的設定就好了
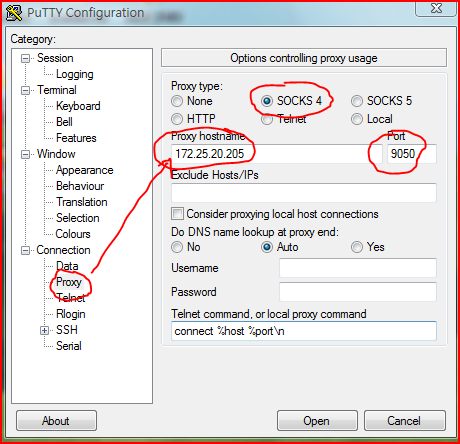
這是透過 tor network 的出口點的 traceroute
8 r02-s2.tp.hinet.net (220.128.4.42) 3.919 ms r02-s2.tp.hinet.net (220.128.4.38) 3.863 ms 3.812 ms
9 r12-pa.us.hinet.net (211.72.108.193) 133.255 ms 133.232 ms *
10 r11-ny.us.hinet.net (202.39.83.105) 253.503 ms 253.630 ms 253.790 ms
11 US-NY-RI-01.chello.com (198.32.160.48) 258.488 ms 255.308 ms 259.752 ms
12 213.46.190.93 (213.46.190.93) 252.272 ms us-nyc01b-rd1-10ge-3-0.aorta.net (213.46.190.177) 252.482 ms 252.557 ms
13 213.46.190.50 (213.46.190.50) 258.266 ms * 258.407 ms
14 fr-par02a-rd1-pos-2-0.aorta.net (213.46.160.105) 339.525 ms 339.944 ms 339.758 ms
15 ch-gva01a-ra1-xe-1-0-0.aorta.net (213.46.160.26) 352.450 ms 352.673 ms 352.191 ms
16 mlrZHZ006-xge-3-4.aorta.net (213.46.171.54) 357.266 ms 362.542 ms 355.218 ms
17 * * *
18 80-218-145-22.dclient.hispeed.ch (80.218.145.22) 505.819 ms 508.504 ms 544.136 ms
首先這是 iSCSI 的基本知識 , From wiki : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISCSI
iSCSI uses TCP/IP (typically TCP ports 860 and 3260). In essence, iSCSI simply allows two hosts to negotiate and then exchange SCSI commands using IP networks. By doing this, iSCSI takes a popular high-performance local storage bus and emulates it over wide-area networks, creating a storage area network (SAN). Unlike some SAN protocols, iSCSI requires no dedicated cabling; it can be run over existing switching and IP infrastructure. As a result, iSCSI is often seen as a low-cost alternative to Fibre Channel, which requires dedicated infrastructure.
Although iSCSI can communicate with arbitrary types of SCSI devices, system administrators almost always use it to allow server computers (such as database servers) to access disk volumes on storage arrays. iSCSI SANs often have one of two objectives:
Storage consolidation
Organizations move disparate storage resources from servers around their network to central locations, often in data centers; this allows for more efficiency in the allocation of storage. In a SAN environment, a server can be allocated a new disk volume without any change to hardware or cabling.
Disaster recovery
Organizations mirror storage resources from one data center to a remote data center, which can serve as a hot standby in the event of a prolonged outage. In particular, iSCSI SANs allow entire disk arrays to be migrated across a WAN with minimal configuration changes, in effect making storage “routable” in the same manner as network traffic.
以下是基本的名詞解釋
Further information: SCSI initiator
An initiator functions as an iSCSI client. An initiator typically serves the same purpose to a computer as a SCSI bus adapter would, except that instead of physically cabling SCSI devices (like hard drives and tape changers), an iSCSI initiator sends SCSI commands over an IP network. An initiator falls into two broad types:
An iSCSI host bus adapter (more commonly, HBA) implements a hardware initiator. A typical HBA is packaged as a combination of a Gigabit (or 10 Gigabit) Ethernet NIC, some kind of TCP/IP offload technology (TOE) and a SCSI bus adapter, which is how it appears to the operating system.
An iSCSI HBA can include PCI option ROM to allow booting from an iSCSI target.
iSCSI refers to a storage resource located on an iSCSI server (more generally, one of potentially many instances of iSCSI running on that server) as a “target”. An iSCSI target usually represents hard disk storage. As with initiators, software to provide an iSCSI target is available for most mainstream operating systems.
Special names refer to both iSCSI initiators and targets. iSCSI provides three name-formats:
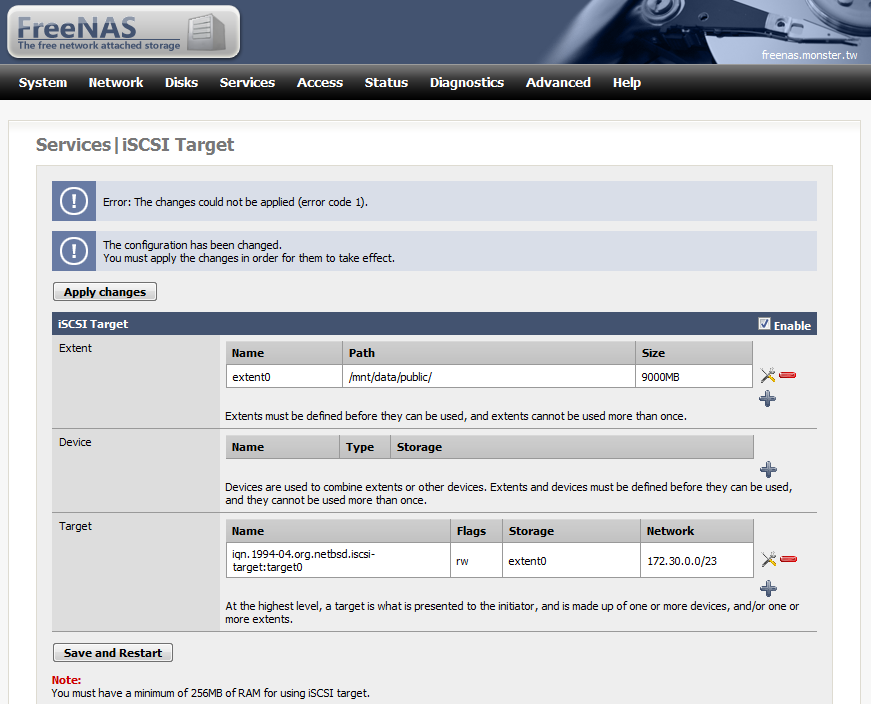
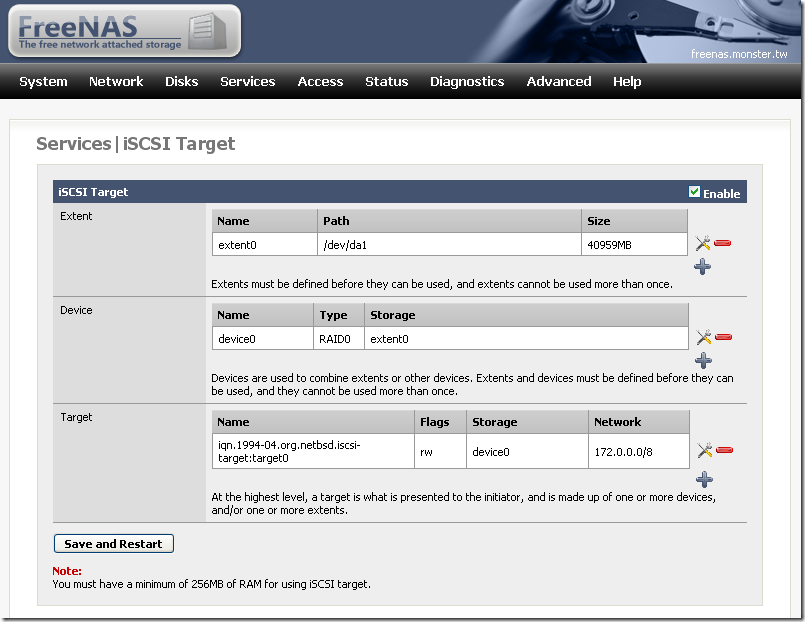
以下是用 FreeNAS 的 step by step ,
我把一個 hardisk 整個當作一個 iSCSI 的 target (FreeNAS 那邊可以分成用 file 或 device 當 target , 各有好壞 , 當然 device 是效能較好)
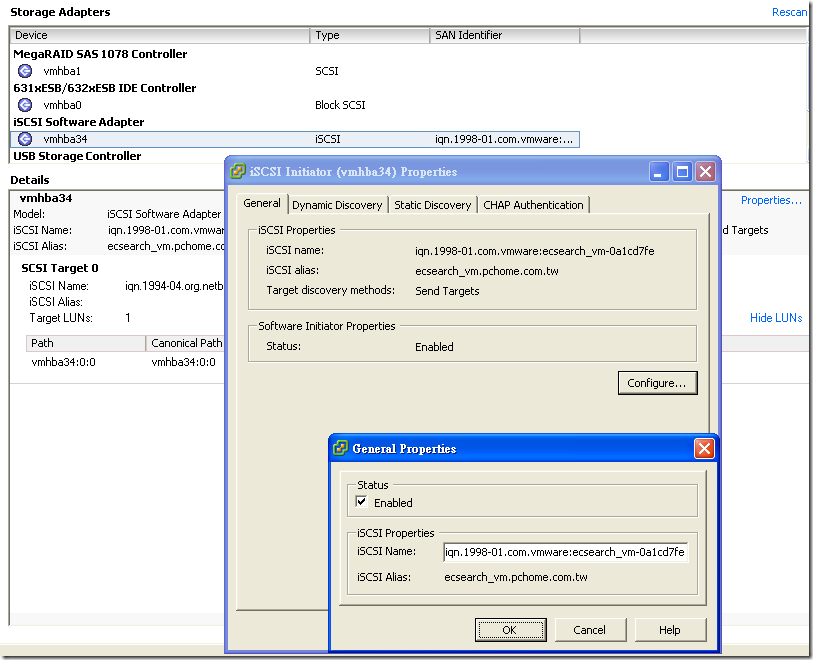
在 VMware ESXi server 那邊要把 iSCSI 的 software adapter enable ( Initiator ):
在 Storage 那邊把 FreeNAS 提供的 iSCSI target 加進來 , Windows Vista 可以直接把 taget 加進去, XP 或 其他的 Windows server 要裝 Microsoft 所題供的 iSCSI software 才行.
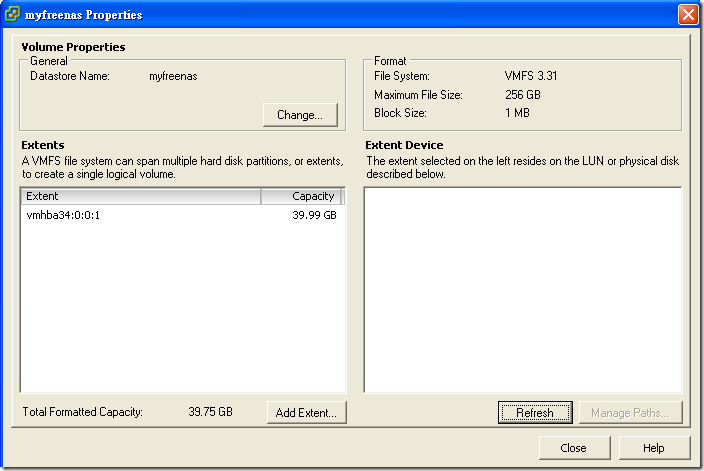
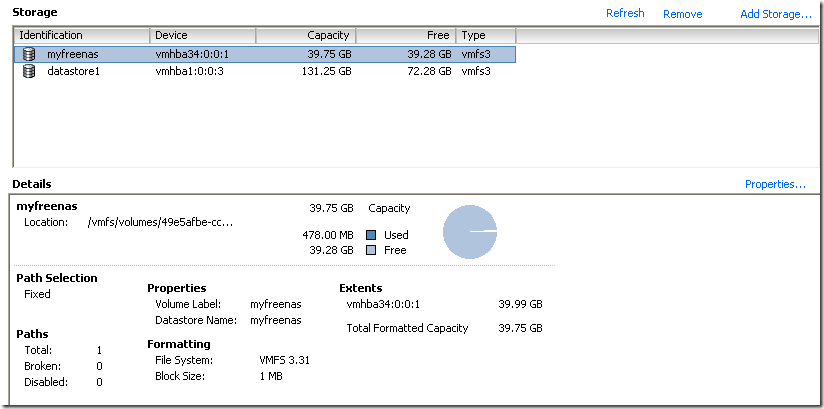
不過我發現 iSCSI 的 extent 用 file 的會有 error : Error: The changes could not be applied (error code1).